Basic Electrical Engineering MCQ Part 2
Point Source Example
The figure below displays an electric circuit drawn using point source:

The voltmeter connected across 15 kohm resistor will read:
- 3 V
- 5 V
- 10 V
- 15 V
Correct answer: 4. 15 V
Explanation:
The circuit redrawn to normal circuit as follows:
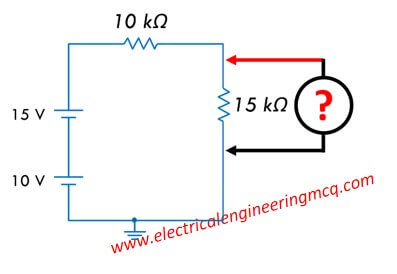
Total input: Vin = 25 V
Using voltage divider rule:
V (15k) = (15 kohm)/(10 kohm + 15 kohm) * 25 V = 15 V
Resistance calculation for 5 ohms wire whose length is increased four times and area by two times
A certain length of wire has resistance 5 ohms. What is the resistance of wire that is made of the same material and is four times longer and has twice the cross-sectional area:
- 2.5 ohms
- 5 ohms
- 7.5 ohms
- 10 ohms
Correct answer: 2 ohms
Explanation: Suppose R1 and R2 are values of resistances and R1 = 5 ohms.
From Formula R1 = ρ*l1/a1 and R2 = ρ*l2/a2
R2/R1 = (l2/l1) * (a1/a2)
R2/R1 = (4.l/l) * (a/2a) = (4.l/l) * (a/2a) = 4/2 = 2
R2 = 2.R1 = 2. 5 ohms = 10 ohms
For constant resistor by increasing the voltage the current will
For constant resistor, by increasing the voltage, the current will:
- Increase
- Decrease
- Remain the same
Correct answer: 1. Increase
3 mA current flowing through 1 kohm resistance will produce a voltage drop of
3 mA current flowing through 1 kohm resistance will produce a voltage drop of:
- 0.33 V
- 1 V
- 3 V
- 3 mV
Correct answer: 3. 3 V
Norton theorem is ___________ Thevenin theorem
Norton’s theorem is ___________ Thevenin’s theorem:
- Identical to
- Converse of
Correct answer: 2. Converse of
Explanation:
Statement of Norton’s theorem: A linear bilateral network can be reduced to a simplified two-terminal circuit consisting of a single current source and a single shunt resistor
Statement of Thevenin Theorem: A linear bilateral network can be reduced to a simplified two-terminal circuit consisting of a single voltage source and a single series resistor