Basic Electrical Engineering MCQ Questions on Current divider rule.
SI unit of current is
SI unit of current is:
- volts
- ohms
- watts
- amps
Correct answer: 4. amps
Current always divide in
Current always divides in:
- Series
- Parallel
Correct answer: 2. Parallel
Current divider rule is applicable on
Current divider rule is applicable on:
- Series circuits
- Parallel circuits
Correct answer: 2. Parallel
For two parallel resistors having same resistance the current will
For two parallel resistors having same resistance the current will:
- Remain same
- Divide
Correct answer: 1. Remain same
Which of the following is correct formula for current divider
Which of the following is correct formula for current divider:
- Ix = (Rx/Req) * It
- Ix = (Req/Rx) * It
- Both of these
- None of these
Correct answer: 2. Ix = (Req/Rx) * It
Current Divider Rule MCQ#6
For current divider circuit give below, if R1 = R2 then:
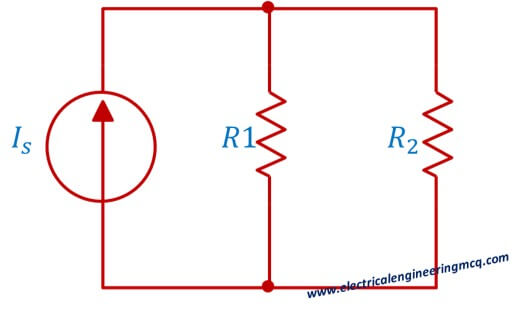
- I1 > I2
- I1 < I2
- I1 = I2
- Insufficient data
Correct answer: 3. I1 = I2
Current Divider Rule MCQ#7
For the same circuit given in problem 6, if R1 > 10R2, for any value of source current, the majority of current will flow through:
- R1
- R2
Correct answer: 1. R2
Current Divider Rule MCQ#8
Current divider rule is never applied to series circuits because:
- It requires application of very complex formulae
- Current never divides in series
Correct answer: 2. Current never divides in series
Current Divider Rule MCQ#9
For current divider circuit in problem 6, If Is = 2 A and R1 = 3 Ω and R2 = 2 Ω and I1 and I2 are values of currents flowing through R1 and R2, then:
- I1 = 1.2 Ω, I2 = 0.8 Ω
- I1 = 1.5 Ω, I2 = 0.5 Ω
- I1 = 1.3 Ω, I2 = 0.7 Ω
- I1 = 0.8 Ω, I2 = 1.2 Ω
Correct answer: 4. I1 = 0.8 Ω, I2 = 1.2 Ω
Current Divider MCQ#10
For circuit given in problem 6, if another resistor is added in series to R2, the current flowing through R1 will:
- Increase
- Decrease
- Remain same
Correct answer: 1. Increase
By increasing resistance there will be reduction of current in R2. To understand this Consider initially current source is of 5A and resistor R1 is of 2 ohms, while R2 is also 2 ohms.
Now current across R1 is: 2.5 A; (I1 = (Req/R1) * It = (1/2) * 5 A = 2.5 A
Now suppose another resistor (having resistance 1 ohms is added in series to R2. Now current across R1:
I1 = (Req/R1) * It = (1.2/2) * 5 A = 3 A