Electrical Engineering multiple choice questions on Transistor Biasing.
Transistor biasing represents the use of which condition
Transistor biasing represents the use of:
- AC conditions
- DC conditions
- Both of above
- None of above
Correct answer: 2. DC conditions
The terms biasing a transistor means the use of DC voltage for establishing the certain operating conditions in a transistor
What does operating point or Q point represent in Transistor Bias
The operating point or Q point represents:
- Peak values of the sine wave
- Zero signal values of IC and VCE
- Values at which IC is maximum and VCE is minimum
- Values at which IC is minimum and VCE is maximum
Correct answer: 2. Zero signal values of IC and VCE
Proper amplification of Silicon diode by transistor circuit
For proper amplification by a transistor circuit, what should be the value of VBE for a silicon diode should:
- Be Zero
- Be as low as possible
- Not fall below 0.7 V
- Be greater than 1.4 V and lesser than 2.8 V
Correct answer: 3. Not fall below 0.7 V
For proper amplification by a transistor circuit, what should be the value of VBE for a silicon diode should not fall below 0.7 V
Which of the following is correct about operating point and the A.C load line
Which of the following is correct about operating point and the A.C load line:
- The operating point lies on load line
- The operating point doesn’t lie on load line
- The operating point may or may not lie on load line
Correct answer: 1. The operating point lies on load line
Voltage Divider Bias Numerical Problem
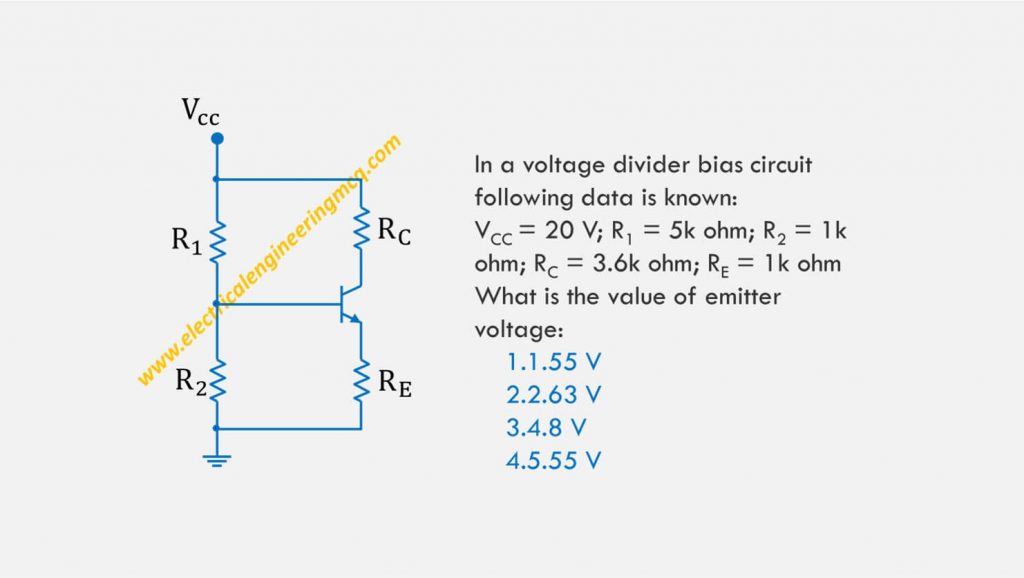
In a voltage divider bias circuit following data is known:
VCC = 20 V; R1 = 5k ohm; R2 = 1k ohm; RC = 3.6k ohm; RE = 1k ohm
What is the value of emitter voltage:
- 1.55 V
- 2.63 V
- 4.8 V
- 5.55 V
Correct answer: 2. 2.63 V
Solution: V2 = {(VCC)/(R1 + R2 ) } * R2
= (20/6)*1 = 3.33 V
Emitter voltage = V2 – VBE = 3.33 – 0.7 = 2.63 V